Your Comprehensive Guide to Medical School Applications
Embarking on your journey to medical school is an exciting yet challenging endeavour. As you prepare to take the next step towards your dream career in medicine, it’s essential to understand the intricacies of the application process. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll provide you with an overview of the key components of a medical school application and offer valuable insights to help you navigate each stage with confidence.
Understanding the Application Timeline
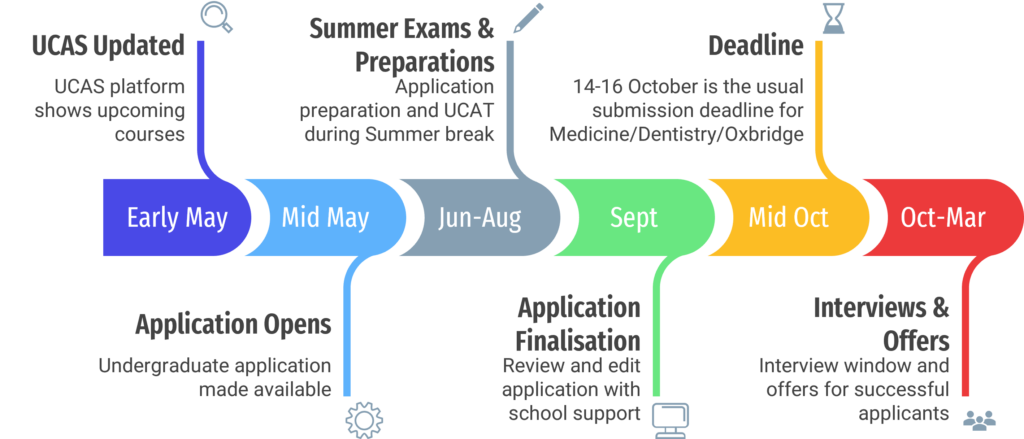
Understanding the application timeline is essential for aspiring medical students to effectively plan and prepare for their journey into medical school. The timeline typically begins well in advance of the application deadline, often spanning several months or even years. It begins with thorough research into prospective medical schools, their entry requirements, and application deadlines. This initial phase allows applicants to identify appropriate medical schools and understand which aspects of their applicaiton needs more work.
Once prospective medical schools have been identified, applicants must allocate time for academic preparation, admissions test registration, and undetake work experience/volunteering work. Reference letters and letters of recommendations should also be planned well in advance to prevent delays. As the application deadline approaches, candidates must carefully compile all required materials, including personal statements, academic evidence, and supplemental application documents. By adhering to the application timeline and staying organised throughout the process, applicants can maximise their chances of securing admission to their desired medical schools.
Entry Requirements
Navigating the entry requirements and prerequisites is crucial for aspiring medical school applicants, as each institution may have unique criteria for admission. Medical schools in the UK and Europe typically provide undergraduate medical courses, where applicants are in their final year of secondary education. Institutions often provide specific guidance for common secondary school qualifications such as GCSEs, GCE/A Levels, IB, and ATAR. There is usually a requirement for candidates to have studied chemistry, maths, and/or biology.
Graduate Entry Medicine (GEM) is an alternative, and is similar to US medical schools and require candidates to have a bachelor’s degree (or above). For graduate entry programs, applicants may also need to demonstrate proficiency in prerequisite subjects such as biology, chemistry, physics, and mathematics. This is often assessed using within the standardised admissions tests that candidates are required to sit depending on the region and specific institution and will be discussed below.
Medical school applicants must also fulfill non-academic requirements, including work experience in healthcare settings, voluntary service, and extracurricular involvement that demonstrates their commitment and skills. By familiarising themselves with the entry requirements and prerequisites of prospective institutions, applicants can tailor and align their efforts to the expectations of admissions committees and improve their chances of securing and interview and offer.
Admissions Tests
Admission tests play a pivotal role in the medical school application process, serving as benchmarks for assessing candidates’ aptitude, critical thinking skills, and readiness to meet the demands of medical education. The UK Clinical Aptitude Test (UCAT) is a widely recognised assessment used by many medical schools in the UK and abroad to evaluate applicants’ cognitive abilities, including problem-solving, logical reasoning, and quantitative analysis. Similarly, the Casper (Computer-based Assessment for Sampling Personal Characteristics) test is increasingly adopted by medical schools to assess non-academic attributes such as professionalism, empathy, and ethical decision-making. These tests are crucial components of the application process, requiring thorough preparation and strategic approach to achieve optimal results.
In addition to the UCAT and Casper, aspiring medical students may also encounter the Medical College Admission Test (MCAT) and the Graduate Medical School Admission Test (GAMSAT), which are commonly used in the United States and Australia, respectively. The MCAT assesses candidates’ knowledge of biological and physical sciences, critical analysis, and reasoning skills, while the GAMSAT evaluates aptitude in science, problem-solving, and written communication. These standardised tests serve as comprehensive assessments of candidates’ academic readiness and intellectual capabilities, providing medical schools with valuable insights into applicants’ potential for success in medical education. Understanding the format, content, and scoring criteria of these admission tests is essential for applicants to effectively prepare and perform at their best on test day.
Personal Statement and Letters of Recommendation
Crafting a compelling personal statement is a pivotal aspect of the medical school application process, allowing applicants to articulate their motivations, experiences, and aspirations to admissions committees. This was traditionally assessed as a short free-form essay about your experiences and reasons for applying but UCAS has recently announced reforms to the admissions approach within the UK. The new questions format presents a structured framework for applicants to address key aspects of their candidacy. Addressing the motivation for the chosen courses, applicants can elucidate their passion for medicine and dentistry, highlighting formative experiences and intrinsic interests that have shaped their career aspirations. Demonstrating preparedness for the courses involves reflecting on past academic achievements, extracurricular engagements, and professional experiences that have equipped applicants with the requisite skills and knowledge to thrive in medical education. Applicants can still integrate their diverse experiences into these questions to showcase their how their experiences and reflections have shaped their abilities, interests, and aspirations. Addressing extenuating circumstances provides applicants with an opportunity to contextualise their achievements and setbacks so that admissions teams can evaluate applicants more holistically.
面試準備
Preparing for medical school interviews, whether they follow a traditional panel format or the Multiple Mini Interview (MMI) structure, demands thorough groundwork and strategic planning. Panel interviews typically involve face-to-face interactions with a multiple interviewers, where candidates respond to a series of questions covering various aspects of their background, experiences, and motivations. To excel in panel interviews, candidates must articulate their thoughts clearly, demonstrate empathy, and exhibit professionalism while showcasing their medical knowledge and awareness of topical issues. Practicing mock panel interviews, seeking feedback, and refining communication skills are essential components of effective preparation for this interview format, allowing candidates to present themselves confidently and authentically during the actual interview.
On the other hand, MMI interviews are now used across most medical schools. MMI involves having candidates navigate through a series of short, station-based encounters, each centered around a specific scenario or task. MMI scenarios will share the assessment of candidates’ communication skills, problem-solving abilities, ethical decision-making, teamwork, and resilience across the different scenarios. Successful candidates are typically able to think quick on their feet, adapt to unexpected scenarios, and effectively communicate their critical thinking. Engaging in MMI-specific preparation, such as practicing timed station rotations, familiarising with common MMI scenarios, and honing interpersonal skills, can significantly improve MMI performance and confidence on the day. By mastering the nuances of both panel and MMI interview formats, aspiring medical students can showcase their best self and performance to the medical school admissions team.
Financial Considerations
Navigating the financial aspects of medical school can be daunting, and it’s essential to consider the cost of tuition, living expenses, and potential sources of financial aid. We’ll discuss various financial considerations associated with medical school, including tuition fees, scholarships, loans, and bursaries, empowering you to make informed decisions about your financial future.
Conclusion
Embarking on your medical school application journey is a significant milestone that requires careful planning, preparation, and perseverance. By understanding the key components of the application process and equipping yourself with the necessary knowledge and resources, you can navigate the journey with confidence and increase your chances of success. Remember, your journey to medical school is unique, and with dedication and determination, you can turn your aspirations into reality.